Best Time to Take Creatine

SIGN UP FOR YOUR FREE DAY PASS TODAY!
Creatine is a molecule stored in muscles, which is converted into phosphocreatine to provide energy for short, high-intensity activities like sprinting, jumping, weightlifting, and various team sports.
Sources of Creatine
Creatine is found in foods like red meat, poultry, fish, and milk. Additionally, your body synthesizes creatine from the amino acids arginine, glycine, and methionine.
The Need for Creatine Supplementation
Engaging in high-intensity sports can deplete your phosphocreatine levels, potentially leading to a deficiency that affects performance.
Supplementing with creatine may enhance muscle mass, boost athletic performance, aid recovery post-exercise, and assist in injury rehabilitation.
Popularity and Forms of Creatine
Creatine is a widely used supplement among gym-goers and athletes, with creatine monohydrate being the most researched and common form.
Its effectiveness and safety can vary based on individual differences, timing of intake, and the dosage taken.
Timing of Creatine Intake
Pre-Exercise Benefits
Research on the timing of creatine supplementation is limited, but some physiological mechanisms suggest benefits from pre-exercise supplementation.
Exercise increases blood flow, which might lead to greater creatine uptake by muscles during activity.
Blood creatine levels peak 1-2 hours after ingestion, remaining elevated for about four hours when 5 grams are consumed. This makes it feasible to take creatine before or even during a workout lasting 40 to 90 minutes.
Post-Exercise Benefits
It's hypothesized that muscles may absorb more creatine during and after exercise. Creatine transporters become more active during physical activity, potentially enhancing uptake.
Comparing Timing Options
In studies involving older adults, those taking creatine immediately before or after resistance training sessions showed increased muscle strength compared to a placebo group.
However, participants who took creatine post-training gained more muscle mass.
Similar benefits were observed in athletes who consumed 5 grams of creatine an hour before or after workouts.
More research is required to definitively determine the optimal timing for creatine supplementation, as both options positively impact muscle mass and strength.
Creatine on Rest Days
Some protocols recommend taking creatine on both training and rest days, but studies have shown benefits when it's taken only on training days.
This approach can reduce costs and avoid unnecessary use, though its impact on effectiveness is still uncertain.
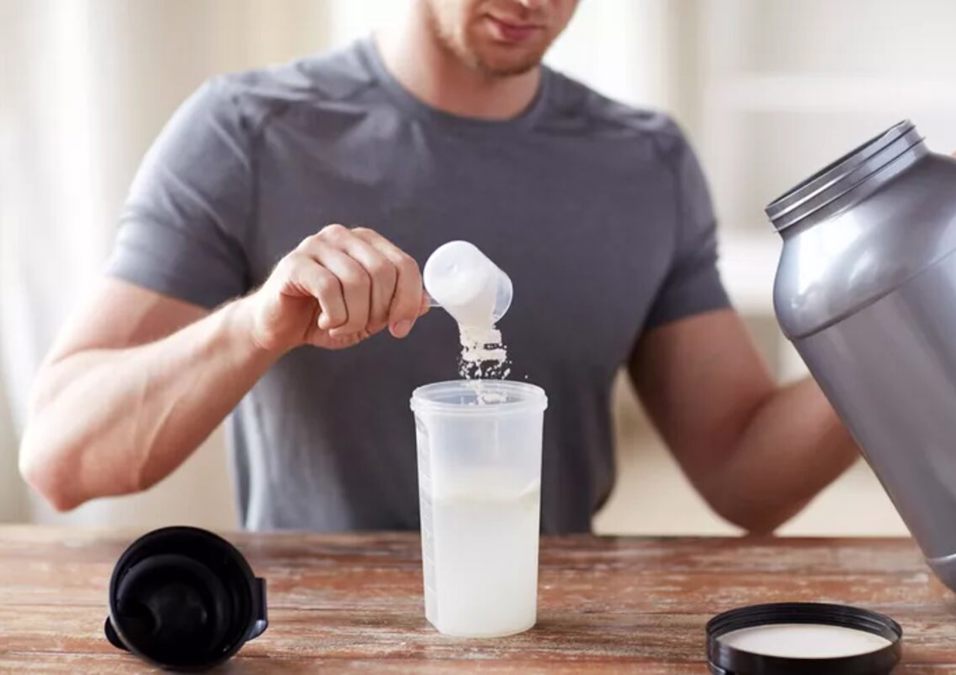
How to Take Creatine
Creatine can be consumed with or without food, but taking it alongside carbohydrates or a combination of carbohydrates and proteins can enhance muscle creatine storage.
Combining creatine with beta-alanine may improve its effects, while caffeine might hinder them, although evidence is not definitive.
Recommended Dosages
Muscle creatine stores can be increased by 20%-40% through supplementation. Two common methods include:
- Loading Dose: Take a high dose of 5 grams of creatine, four times daily (totaling 20 grams per day) for five to seven days. Alternatively, calculate your dose as 0.3 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Maintenance Dose: Follow up with a daily dose of 3 to 5 grams or calculate it as 0.1 grams per kilogram of muscle mass.
For instance, with 40 kg of muscle, you'd take 4 grams daily. Another protocol suggests taking 3 grams daily for 28 days, resulting in gradual muscle creatine increase but slower performance gains.
Safety Considerations
While creatine can improve muscle mass, strength, and recovery, further research is needed to fully understand its efficiency and safety.
Potential concerns include water retention, dehydration, kidney health, hair loss, muscle cramping, and its effects on women.
Summary
Creatine can boost muscle mass, strength, and recovery, but there's no conclusive evidence favoring a specific intake timing.
Benefits can be achieved by consuming it either before or after exercise. How much you gain from creatine depends on factors like age, gender, health, diet, supplementation protocol, and the type, intensity, and volume of your training.
Source: health
The opinions shared in the GymNation blog articles are solely those of the respective authors and may not represent the perspectives of GymNation or any member of the GymNation team.