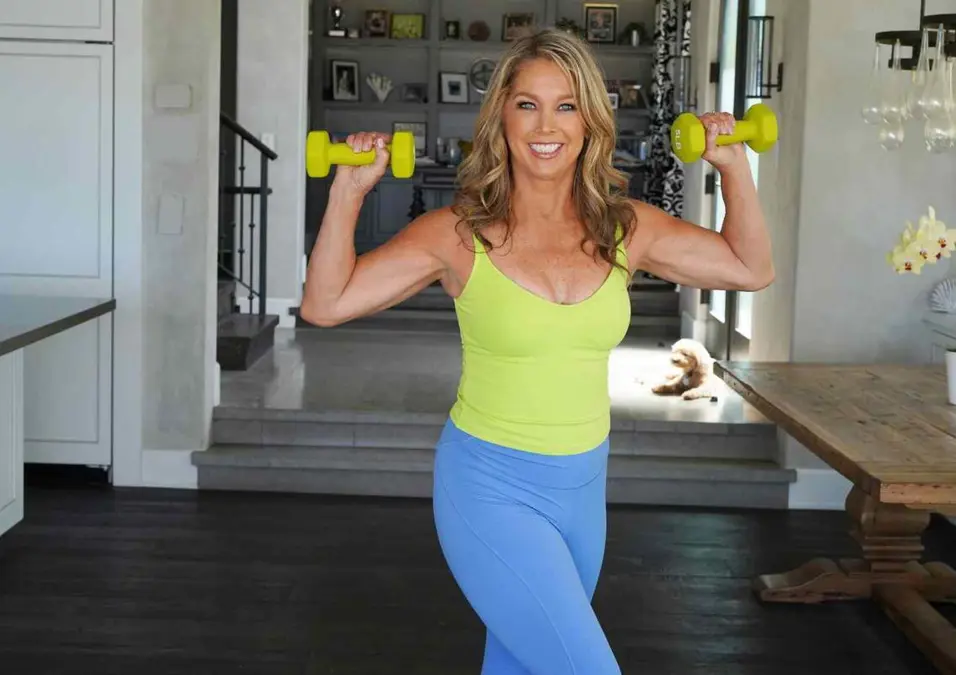
Building Muscle After 50

SIGN UP FOR YOUR FREE DAY PASS TODAY!
Building muscle after 50 plays a crucial role in maintaining strength and overall health. Along with staying consistent with strength training and consuming enough protein, many wonder how long it actually takes to build muscle.
According to Dotsie Bausch, C.P.T., sports nutritionist, Olympian, and founder of Switch4Good, "Building and retaining muscle isn’t just about aesthetics. It ensures vitality, long-term health, and resilience.
Muscle is metabolically active tissue that supports metabolism, regulates blood sugar, maintains joint health, and shields against falls and fractures as we age."
She emphasizes the significance of muscle for women, explaining that the natural decline in muscle mass makes building and maintaining it even more essential.
"Muscle is your fountain of youth, and no matter your age, you can always build it," she adds.
Here’s a breakdown of how muscle growth works and expert guidance on optimizing your muscle-building process.
Read More: Building a Body Like Ben Shephard at 50
How Do Muscles Grow?
When you engage your muscles through lifting weights, resistance exercises, or cardio activities, tiny tears form in the muscle fibers. While this might sound harmful, it’s a positive process.
"Your body repairs and rebuilds these fibers stronger than before, a process called muscle protein synthesis," explains Bausch.
"This repair process is powered by nutrition, particularly protein, which provides essential amino acids as building blocks." Muscle growth thrives on this cycle of breakdown and rebuilding.
Read More: A 50-Year-Old Mother of Two Defies Odds in Bodybuilding Debut
Factors That Influence Muscle Growth
Muscle growth isn’t purely based on exercise; various factors come into play, including diet, activity, rest, and even genetics.
Diet:
Your diet is pivotal. Adequate calories and protein are essential. Research shows that consuming 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight supports muscle development.
While animal products are commonly associated with high protein content, plant-based foods like tofu, lentils, beans, and soy milk also contribute effectively for those on vegan diets.
Exercise:
Consistent resistance training is key. "Progressive overload is essential, meaning you gradually increase the resistance or intensity of your exercises," says Bausch.
Combining compound movements (like squats or deadlifts) with functional exercises adds variety, helping develop a balanced physique.
Sleep:
Recovery happens during deep sleep. Aim for seven to nine hours of quality sleep nightly.
Deep sleep promotes the release of growth hormones, which are critical for muscle repair and growth.
Age:
With age, muscle mass naturally decreases, a phenomenon called sarcopenia. However, regular strength training counteracts this decline.
"Older adults can build muscle, but they need a more intentional approach," Bausch says.
Genetics:
While genetics may affect the pace of your progress, everyone can gain muscle with the proper routine.
"No one is genetically incapable of building muscle, but for some, it might take longer," Bausch explains.
How Long Does it Take to Build a Pound of Muscle?
For beginners, gaining one to two pounds of muscle per month is typical, as the body responds actively to new stimuli.
For seasoned lifters, the rate slows to 0.25 to 0.5 pounds monthly. This decrease is due to the body's adaptation over time, making progressive overload immensely important.
To build a pound of muscle effectively, focus on these principles:
- Train with progressive overload three to five times weekly.
- Fuel your muscles with enough calories and protein.
- Prioritize sleep and set aside rest days.
Resistance vs. Repetitions
A common question when working out is whether to prioritize heavier weights or perform more repetitions. Both contribute to muscle growth.
For the best results, try six to 12 repetitions per set, using a resistance level challenging enough that the last two or three reps are tough to complete.
Perform three to five sets per exercise, two to three times per week, and incrementally increase either the resistance, repetitions, or sets over time.
Why Rest Matters
Muscle recovery is just as important as the workouts themselves. Growth hormones are released during sleep, aiding in recovery. Similarly, rest days allow recovery and prevent overtraining, which can hinder growth.
"Your muscles repair and grow stronger during rest, so proper recovery is an integral part of any muscle-building program," says White.
What Role Does Nutrition Play in Muscle Growth?
Nutrition is the foundation of your muscle-building efforts. Protein helps rebuild muscle tissue post-workout, and calories provide the energy necessary for this process.
Experts recommend consuming 0.7 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight evenly throughout your day.
"The strategy is simple," says White. "Each meal should include 20-40 grams of high-quality protein every three to five hours."
Cardio and Muscle Growth
Questions often arise about whether cardio hinders muscle growth. Cardio, when balanced, is beneficial. It boosts cardiovascular health, aids in endurance, and promotes recovery.
However, excessively long cardio sessions that burn too many calories may interfere with muscle-building goals.
White recommends moderate cardio activities like walking or cycling, performed two to three times per week, to complement your routine.
Takeaway
Building muscle after 50 is entirely achievable and vital for maintaining health, energy, and resilience.
While results vary based on factors such as nutrition, exercise habits, sleep, and age, dedication to progressive resistance training, proper recovery, and a protein-rich diet will lead to noticeable improvements.
With consistent effort, muscle truly becomes a lasting source of strength and vitality at any age.
Source: prevention
The opinions shared in the GymNation blog articles are solely those of the respective authors and may not represent the perspectives of GymNation or any member of the GymNation team.
GET YOUR FREE TRIAL TODAY