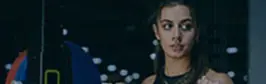Ultimate Push Workout Routine for Strength & Size

SIGN UP FOR YOUR FREE DAY PASS TODAY!
A push workout is a type of strength training routine that focuses on exercises where you push the weight away from your body. This typically includes movements like bench presses, shoulder presses, and triceps extensions. These exercises primarily target the major muscles of the upper body, including the chest, shoulders, and triceps, which are essential for building strength and muscle mass.
The Push-Pull-Legs (PPL) Program is a popular way to organize your training. It divides workouts into three categories: push (chest, shoulders, triceps), pull (back, biceps), and legs (quads, hamstrings, calves). This is considered an efficient workout split because it maximizes muscle building and recovery by grouping exercises that target similar muscle groups together.
Push Workouts:
-
Focus on exercises that involve pushing movements.
-
Target the major muscle groups responsible for pushing, such as the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
-
Help develop upper body strength and muscle definition.
What is a Push Workout?
A push workout is a training session that targets the upper body muscles responsible for pushing movements—primarily the chest, shoulders, and triceps. This approach is a fundamental component of the Push-Pull-Legs (PPL) training split, which is a type of training split that organizes workouts based on movement patterns to enhance muscle balance and recovery.
Push vs Pull vs Legs: Quick Breakdown
-
The PPL split divides workouts into three distinct categories:
-
Push Workouts: Focus on exercises that involve pushing weights away from the body, engaging the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Examples include bench presses, overhead presses, and push-ups.
-
Pull Workouts: Emphasize pulling movements that work the back, biceps, and forearms. Pull exercises include movements like pull-ups, rows, and bicep curls, which involve pulling weight toward the body.
-
Leg Workouts: Target the lower body muscles, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, through leg exercises like squats, deadlifts, and lunges that are performed to specifically target the leg muscles.
Why Push Days Are Important for Muscle Growth
Incorporating dedicated push days into your workout regimen offers several benefits:
-
Optimized Muscle Recovery: By isolating pushing muscles in a single session, you reduce the risk of overtraining and allow for better recovery, which is crucial for muscle growth.
-
Balanced Muscle Development: Focusing on push exercises ensures that the anterior upper body muscles are adequately trained, promoting symmetry and preventing muscular imbalances.
-
Enhanced Strength Gains: Regularly training push movements can lead to significant improvements in upper body strength, benefiting both athletic performance and daily functional activities.
-
Efficient Training Sessions: Grouping similar muscle groups allows for more efficient workouts, as exercises can be sequenced to maximize performance and minimize fatigue.
Your ideal gym buddy is…
Push Workout Benefits
Muscle Group Isolation & Growth
Push workouts target specific muscle groups—primarily the chest, shoulders, and triceps—allowing for focused training that promotes muscle hypertrophy and strength gains. Consistently targeting the same muscles with a challenging workout is essential for muscle growth and adaptation. By concentrating on these areas, you can achieve balanced upper body development and improved muscular definition.
Which Muscles Are Worked in a Push Workout?
Push workouts primarily target the push muscles, which include the chest, shoulders, and triceps. These muscle groups are responsible for pushing and pressing movements such as bench presses, overhead presses, and push-ups.
Chest Muscles (Pectorals)
The pectoral muscles are the main muscles of the chest. They are heavily engaged during exercises like bench presses, push-ups, and chest flyes.
Shoulder Muscles (Deltoids)
The deltoids are the primary muscles of the shoulders. They play a key role in overhead pressing movements and help stabilize the shoulder joint during push exercises.
Triceps Muscles
The triceps muscle is located on the back of the upper arm and is made up of three heads: the long head, lateral head, and medial head. These heads work together to extend the elbow during pressing movements. Exercises such as lying tricep extensions, barbell lying triceps extension, and variations that emphasize the long head are effective for targeting and developing the triceps muscle.
Best Push Workout Routine: Exercises & Technique
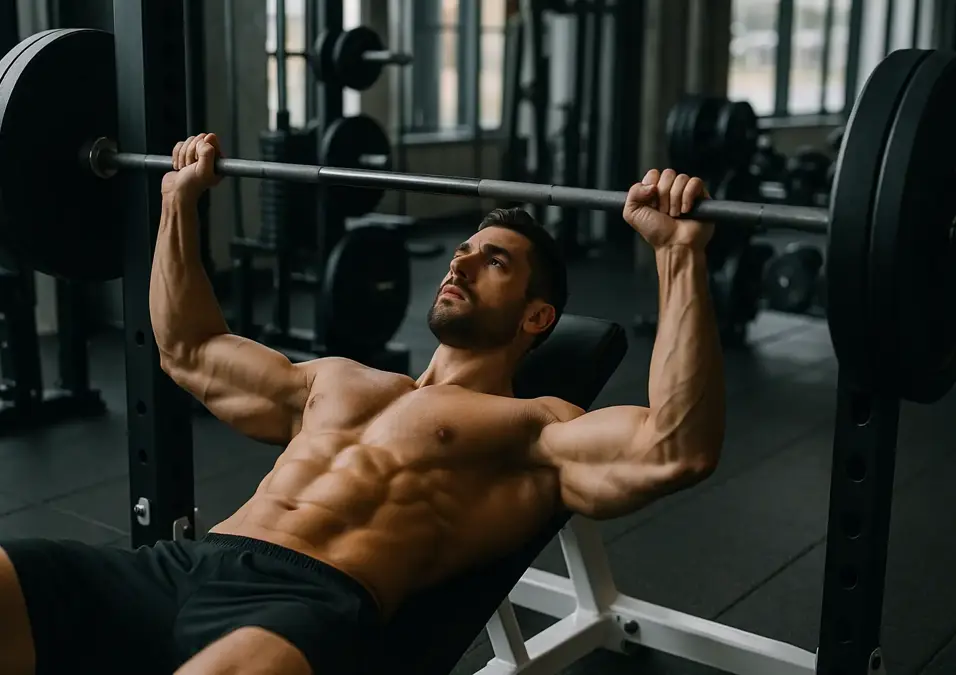
1. Barbell Bench Press
How to Do It (Form Tips):
-
Lie flat on a bench with your feet flat on the ground to ensure stability throughout the movement.
-
Grip the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width, keeping your wrists straight and elbows at a 45-degree angle to your torso.
-
Lower the bar to your mid-chest, maintaining control and keeping your shoulder blades retracted.
-
Press the bar upward until your arms are fully extended, without locking your elbows. Bench pressing involves shoulder flexion and targets the pectoralis major, making it a primary movement for upper body strength. Bench press training is highly effective for increasing muscle thickness in the chest and also contributes to triceps and deltoid development.
Alternatives:
-
Machine Chest Press: Provides guided movement, ideal for beginners or those focusing on form.
-
Push-Ups: A bodyweight alternative that can be modified for different difficulty levels.
-
Close Grip Bench Press: Focuses on triceps strength and muscle development by using a narrower grip, allowing for heavier loads and targeting the triceps muscle heads.
2. Overhead Shoulder Press
How to Do the Overhead Press:
-
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder height with palms facing forward.
-
Engage your core and press the weight overhead until your arms are fully extended.
-
Lower the weight back to shoulder height with control, focusing on maintaining proper mechanics at the shoulder joint to ensure stability and reduce risk of injury.
Alternatives:
-
Seated Dumbbell Overhead Press: Offers back support and reduces lower body involvement.
-
Arnold Press: A variation that incorporates rotation to engage all deltoid muscles and challenges the shoulder joint through a greater range of motion.
3. Incline Dumbbell Press
How to Do It:
-
Set an adjustable incline bench to a 30-45 degree angle. The incline bench press is a key variation for targeting the upper chest.
-
Sit with dumbbells resting on your thighs, then lift them to shoulder height as you lie back.
-
Press the dumbbells upward until your arms are extended, then lower them back to shoulder level. Adjusting the incline bench angle between 15-45 degrees can emphasize upper pec activation and shift muscle engagement between the upper chest and shoulders.
Alternatives:
-
Smith Machine Incline Press: Provides stability and controlled movement.
-
Incline Bench Press: A classic barbell variation for upper chest and shoulder development.
-
Incline Bench Presses with Dumbbells: Offers a greater range of motion and can enhance upper pec activation.
-
Dumbbell Bench Press: A flat or incline variation that targets the chest with increased range of motion.
-
Incline Push-Up: A bodyweight exercise targeting the upper chest.
4. Dumbbell Lateral Raises
How to Do It:
-
The dumbbell lateral raise targets the middle deltoid muscles.
-
Stand with a dumbbell in each hand at your sides, palms facing inward.
-
With a slight bend in your elbows, raise your arms out to the sides until they are just above shoulder level to maximize muscle engagement.
-
Use light weights to maintain proper form and control throughout the lateral raise.
-
Lower the weights back to the starting position with control.
Variations:
-
Cable Lateral Raises: Provide constant tension throughout the movement.
-
Seated Lateral Raises: Reduce momentum, isolating the shoulder muscles more
5. Chest Flyes (Machine or Dumbbell)
How to Do It:
-
Lie on a flat bench holding dumbbells above your chest with palms facing each other.
-
With a slight bend in your elbows, lower the weights out to the sides in a wide arc until you feel a stretch in your chest.
-
Bring the dumbbells back together above your chest, maintaining the arc
6. Triceps Isolation Moves
Cable Pushdowns:
-
Attach a straight or rope handle to a high pulley.
-
Stand facing the machine, grasping the handle with an overhand grip.
-
Keep your elbows close to your sides and push the handle down until your arms are fully extended.
-
Slowly return to the starting position.
-
This triceps exercise targets all three heads of the tricep muscles, making it a staple for triceps development.
Lying Triceps Extension:
-
Lie on a bench holding an EZ bar or dumbbells above your chest.
-
Lower the weight toward your forehead by bending your elbows, keeping your upper arms stationary.
-
Extend your arms back to the starting position.
-
The lying triceps extension is a highly effective triceps exercise that emphasizes the long head of the tricep muscles, promoting muscle growth and strength.
Overhead Triceps Extension:
-
Hold a dumbbell with both hands and lift it overhead.
-
Keep your elbows close to your ears and lower the weight behind your head by bending your elbows.
-
Extend your arms back to the starting position.
Alternative Exercises:
-
To add variety and prevent plateaus, consider alternative exercises such as triceps kickbacks, close-grip bench press, or dips. These alternative exercises also target the tricep muscles and help optimize muscle development.
Push Day 1: Heavy Focus
Objective: This is a typical push day workout, structured to emphasize compound movements and build foundational strength in the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
-
Barbell Bench Press – 4 sets of 6–8 reps (pressing exercise targeting chest, shoulders, triceps)
-
Overhead Barbell Press – 3 sets of 6–8 reps (pressing exercise targeting shoulders, triceps)
-
Incline Dumbbell Press – 3 sets of 8–10 reps (pressing exercise targeting upper chest, shoulders, triceps)
-
Dumbbell Lateral Raises – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
-
Cable Triceps Pushdowns – 3 sets of 10–12
Rest: 60–90 seconds between sets.
Pull Day: Back and Biceps
Objective: This pull workout targets the upper body’s pulling muscles to enhance posture and upper back strength. Incorporating pull exercises in the same workout can efficiently target multiple muscle groups, especially when combined with push or leg exercises for a balanced routine.
-
Deadlifts – 4 sets of 5 reps
-
Pull-Ups or Lat Pulldowns – 3 sets of 8–10 reps
-
Barbell Rows – 3 sets of 8–10 reps
-
Face Pulls – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
-
Barbell or Dumbbell Curls – 3 sets of 10–12
Rest: 60–90 seconds between sets.
Legs Day: Lower Body Strength
Objective: This session focuses on leg exercises for comprehensive exercise training, aiming to develop strength and endurance in the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves.
-
Barbell Back Squats – 4 sets of 6–8 reps
-
Romanian Deadlifts – 3 sets of 8–10 reps
-
Leg Press – 3 sets of 10–12 reps
-
Seated Leg Curls – 3 sets of 10–12 reps
-
Standing Calf Raises – 3 sets of 12–15
Rest: 60–90 seconds between sets.
Push Day 2: Volume and Isolation
Objective: This is one of the push day workouts designed to increase muscle mass by boosting training volume and focusing on muscle hypertrophy in the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
-
Incline Dumbbell Press – 3 sets of 10–12 reps
-
Seated Dumbbell Shoulder Press – 3 sets of 10–12 reps
-
Machine Chest Flyes – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
-
Cable Lateral Raises – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
-
Overhead Triceps Extensions – 3 sets of 12–15 reps
Rest: 45–60 seconds between sets.
Rest or Active Recovery
Objective: Facilitate muscle recovery and prevent overtraining.
-
Light Cardio: 20–30 minutes (e.g., walking, cycling)
-
Mobility Work: Foam rolling and stretching exercises
-
Optional: Yoga or swimming
Weekly Schedule Example:
-
Monday: Push Day 1
-
Tuesday: Pull Day
-
Wednesday: Rest or Active Recovery
-
Thursday: Legs Day
-
Friday: Push Day 2
-
Saturday: Rest or Active Recovery
-
Sunday: Rest
Reps, Sets & Rest: UAE Fitness Guide
How Many Sets & Reps for Muscle Growth
To effectively build muscle (hypertrophy), the following guidelines are recommended:
Repetitions (Reps): Aim for 6–12 reps per set. This range is widely recognized for stimulating muscle growth by balancing tension and fatigue.
Sets: Perform 3–5 sets per exercise. This volume allows sufficient stimulus for muscle development without overtraining.
Intensity: Use a weight that brings you close to muscle failure within the target rep range, ensuring effective muscle.
Adequate protein intake is essential to support muscle growth, recovery, and increases in muscle thickness, especially when following a structured resistance training program.
For beginners, starting with 1–3 sets per exercise, 2–3 times per week, is advisable. As you progress, increasing to at least 10 weekly sets per muscle group can enhance results.
Ideal Rest Time Between Sets
Rest periods between sets are crucial for performance and recovery:
Compound Exercises (e.g., squats, bench press): Rest for 1.5–2.5 minutes to allow adequate recovery for subsequent sets.
Isolation Exercises (e.g., bicep curls, tricep extensions): Shorter rest intervals of 30–90 seconds can be effective, maintaining muscle tension and promoting growth.
Tracking Your Progress at UAE Gyms
Monitoring your fitness journey is essential for sustained progress. Here are effective strategies:
Set SMART Goals: Define Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives to provide clear direction and motivation.
Maintain a Workout Journal: Record exercises, sets, reps, and personal notes to track improvements and identify areas needing adjustment.
Utilize Fitness Apps: Leverage technology to monitor performance metrics, schedule workouts, and receive real-time feedback.
Regular Assessments: Periodically evaluate body measurements, strength levels, and endurance to quantify progress and adapt your training plan accordingly.
At GymNation, our facilities are equipped with the latest tools and technologies to support your fitness tracking needs, ensuring you stay informed and motivated throughout your journey.
Tips to Maximize Push Workout Results
Eat Right: UAE-Specific Nutrition Tips
Building muscle requires a well-balanced diet that aligns with the unique climate and lifestyle of the
-
Prioritize Lean Proteins: Incorporate sources like chicken, fish, lean beef, tofu, and legumes to support muscle repair and growth.
-
Include Complex Carbohydrates: Foods such as whole grains, oats, quinoa, and sweet potatoes provide sustained energy for your workouts.
-
Incorporate Healthy Fats: Avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil are essential for hormone balance and overall health. Stay Hydrated: Given the UAE's hot climate, ensure adequate water intake to support muscle function and recovery.
-
Consider Meal Plans: Services like Energy Meal Plans and WellFed offer muscle gain meal plans tailored for the UAE, providing balanced macronutrients to support your fitness goals.
UAE Gym Equipment Recommendations:
-
Most gyms in the UAE are equipped with pec deck machines and cable stations, offering alternatives for chest flyes.
-
You can use the cable machine to perform cable flyes, which allow for controlled movement and constant tension on the chest muscles.
-
Cable flyes and dumbbell flyes are alternative exercises that target the same muscles, providing variety while working the chest.
-
Stay Consistent & Recover Well
Consistency and recovery are pivotal in achieving muscle growth:
-
Establish a Routine: Aim for regular workouts, focusing on push exercises 2–3 times per week to allow for adequate recovery.
-
Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night to facilitate muscle repair and growth.
-
Incorporate Active Recovery: Engage in light activities like walking or yoga on rest days to promote blood flow and aid recovery.
-
Listen to Your Body: Adjust workout intensity based on how you feel to prevent overtraining and reduce injury risk.
Use Progressive Overload (Safely)
Progressive overload involves gradually increasing the stress placed on your muscles to stimulate growth:
-
Increase Resistance: Gradually add weight to your exercises as you become stronger.
-
Add Repetitions or Sets: Increase the number of reps or sets to challenge your muscles further.
-
Modify Tempo: Slow down the eccentric (lowering) phase of movements to increase time under tension.
-
Ensure Proper Form: Always prioritize correct technique to prevent
Implementing progressive overload should be done thoughtfully to avoid plateaus and minimize injury risks.
Push Workout FAQ
What is a push day workout?
What is the 4-2-1 workout schedule?
The 4-2-1 workout schedule consists of 4 days of strength training, 2 days of cardio, and 1 day of mobility or active rest each week. This balanced routine supports muscle growth, cardiovascular health, and recovery.
Which exercises are push vs. pull?
Push exercises: Involve pushing weight away from the body, working the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Examples: bench press, overhead press, push-ups.
Pull exercises: Involve pulling weight toward the body, engaging the back and biceps. Examples: pull-ups, rows, bicep curls.
What is push workout?
Push workout refers to exercises that involve pushing movements, primarily targeting the chest, shoulders, and triceps. These exercises are essential for upper body strength and functional movements.
What is push vs. pull?
Push exercises involve moving weight away from the body, targeting muscles like the chest and triceps. Pull exercises involve drawing weight toward the body, focusing on the back and biceps. Balancing both ensures comprehensive muscle development.
Is abs push or pull?
Abdominal exercises can involve both pushing and pulling motions. For instance, planks (a push exercise) and crunches (a pull exercise) both engage the core.
Are squats push or pull?
Squats are considered a push exercise. They involve pushing through the heels to extend the hips and knees, engaging the quadriceps and glutes.
Is chest fly push or pull?
Chest flys are generally considered a pushing exercise because they involve extending the shoulder joints.
Are curls push or pull?
Curls are pull exercises. They involve pulling the weight toward the body, primarily working the biceps.
Are dips push or pull?
Dips are push exercises. They target the triceps, chest, and shoulders by pushing the body upward.
Can I do push day every day?
It's not recommended to do push workouts daily. Muscles need time to recover and grow. Incorporating rest days or alternating with pull and leg days ensures optimal results and reduces the risk of overtraining.
GET YOUR FREE TRIAL TODAY