Workouts & Cravings: Science

SIGN UP FOR YOUR FREE DAY PASS TODAY!
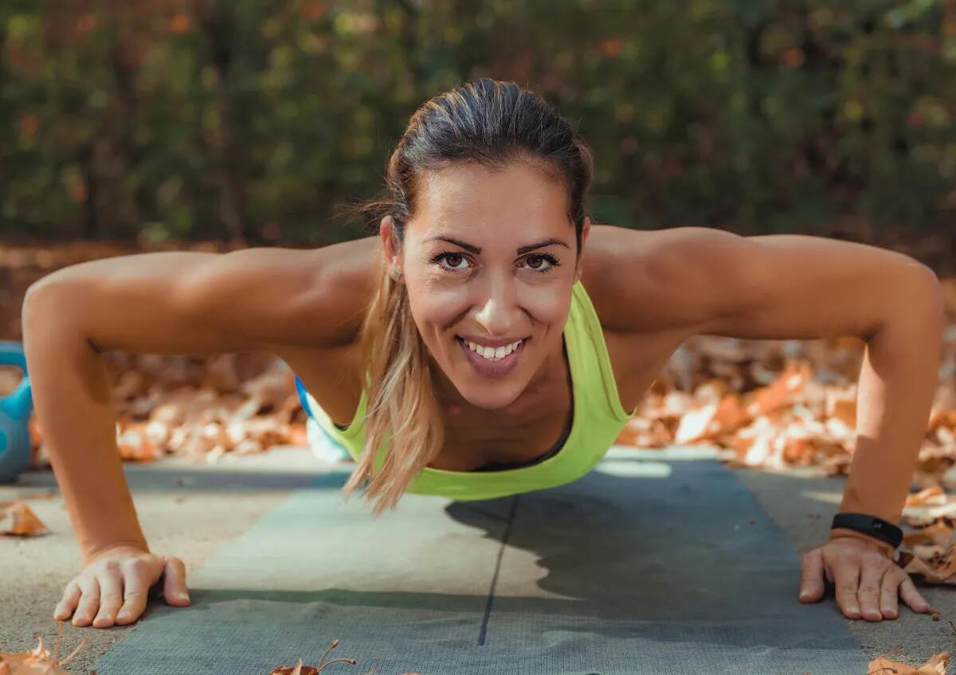
Ever finish an intense HIIT class or a challenging spin session and notice that food is the last thing on your mind? This isn’t a coincidence—there’s science behind this surprising outcome.
While moderate workouts might have you fantasizing about a cheesy pizza mid-session, high-intensity exercise can actually suppress your appetite. Here’s a closer look at why intense workouts might keep those snack cravings at bay.
The Science of Appetite Suppression Post-Workout
Researchers from the University of Virginia studied this phenomenon and shared their findings in the Journal of the Endocrine Society.
They investigated how exercise intensity influences levels of ghrelin, the hormone that triggers hunger, and how this impacts appetite control.
The Effects of High-Intensity Workouts on Hunger
The findings revealed that intense workouts are particularly effective at reducing hunger compared to moderate exercise or simply resting.
“Our research suggests that high-intensity exercise may be important for appetite suppression, which can be particularly useful as part of a weight loss program," explained Kara Anderson, the lead researcher.
On the flip side, gentler activities, such as yoga or a leisurely jog, don’t have as strong an effect on suppressing appetite.
These exercises are easier on the body, so hunger hormones don’t drop in the same way, leaving you more likely to think about food sooner.
Ghrelin: The Hunger Hormone at Work
Ghrelin, often dubbed the "hunger hormone," comes in two varieties within the body:
- Acylated ghrelin (AG): This form signals hunger to the brain, making up about 22% of total ghrelin.
- Deacylated ghrelin (DAG): This appetite-neutral form, which either suppresses appetite or has no effect, represents the remaining 78%.
Aside from controlling hunger, ghrelin also plays roles in energy regulation, blood sugar levels, immune response, sleep, and memory.
By understanding how exercise alters these types of ghrelin, workouts can be tailored for effective weight management.
During intense activity, your body seamlessly redirects its energy. Rather than focusing on digestion, it prioritizes sending blood flow to your muscles, allowing you to push through the challenge.
This switch causes your digestive system to take a temporary break, resulting in less interest in food—at least for a short while.
The Role of Endorphins
During demanding workouts, the body releases endorphins, the "feel-good" hormones responsible for that post-exercise euphoria. Besides improving your mood, these endorphins can also reduce hunger, contributing to the appetite-suppressing effect.
Moderate Workouts and Hunger
Less intense workouts, like yoga or light jogging, have a different impact. Since they’re less taxing on the body, your level of ghrelin doesn’t dip in the same way, so you’re more likely to feel hungry.
According to the research, you might even start thinking about snacks before you’ve finished your cooldown stretches.
How Long Does Appetite Suppression Last?
The appetite-suppressing effects of a high-intensity workout don’t last forever. A few hours post-exercise, hunger typically returns as your body seeks fuel for recovery.
The good news? You’re more likely to crave something nutritious, like protein or complex carbohydrates, instead of sugary junk food.
Should Every Workout Be High-Intensity?
Not necessarily. According to Mehul Jadhav, a fitness nutritionist and trainer based in Dubai, "While intense workouts are effective for short-term appetite suppression, they’re just one part of the fitness equation.
Moderate workouts offer their own unique benefits, including stress relief and sustained energy.
The key is balancing exercise types to suit your goals, and don’t forget to eat properly—your body needs the right fuel to recover and thrive."
Smarter Choices for Workouts and Nutrition
By recognizing how different workout intensities affect hunger, you can align your exercises with your health and fitness goals.
Whether you’re aiming for weight management or overall wellness, understanding the science behind these effects can help you stay on track and feel your best.
Source: gulfnews
The opinions shared in the GymNation blog articles are solely those of the respective authors and may not represent the perspectives of GymNation or any member of the GymNation team.
GET YOUR FREE TRIAL TODAY