Dumbbell Bench Press
Dumbbell Bench Press Video Guide
The dumbbell bench press is a bench press variation that builds chest strength and muscle mass while also strengthening the triceps brachii and anterior deltoid. Compared with the barbell bench press, dumbbells allow a greater range of motion and more natural shoulder positioning, which improves shoulder stability and reduces joint stress. Because each dumbbell moves independently, the exercise develops unilateral strength, helps correct left–right imbalances, and supports balanced chest and shoulder development.
A well-structured bench press plan or workout routine that incorporates variations like the dumbbell bench press and incline bench press can help lifters build strength, increase muscle mass, and progress toward balanced upper-body development. The dumbbell bench press fits into different training goals — whether you want to increase muscle size, improve pressing power, or enhance stability.
Using a strong starting position — feet flat on the floor, shoulder blades retracted, palms facing forward, neutral grip in the wrists, and a slight arch to maintain proper form — the dumbbell chest press activates key muscle groups across the upper chest, mid-chest, pectoralis major, triceps, anterior deltoids, and upper arms. Engaging the lower body for stability is essential for optimal performance and joint protection, while also improving core stability.
Compared to a barbell press, lifters often can’t press as much weight, but they gain superior range of motion, cleaner movement patterning, and improved muscle activation. The stabilising muscles work harder, increasing control, lowering injury risk, and improving pressing mechanics. The dumbbell bench press is especially suitable for those with shoulder issues, as it allows for a more natural movement path and reduces stress on the joint. Whether the goal is a more sculpted chest, improved functional pressing strength, or balanced upper-body muscle development, the dumbbell bench press remains one of the most effective exercises for building muscle mass and fixing strength imbalances.
How to Perform the Dumbbell Bench Press
-
Sit on the bench with a dumbbell resting on each thigh. Lie back and bring the weights into the starting position with palms forward and wrists neutral.
-
Retract the shoulder blades, keep feet flat on the floor, and maintain a slight arch for shoulder health and better core stability. Drive feet into the floor and tighten the glutes for added power and stability.
-
Lower both dumbbells in a controlled motion with elbows tucked, keeping constant tension on the chest muscles.
-
Push and lift the dumbbells upward in a straight path until arms extend (without forceful locking). This keeps bar-style control while still using dumbbells.
-
Repeat for prescribed reps, keeping even tension to build stronger unilateral strength and balanced upper-body power.
GymNation Tip: Maintain consistent bar-path-style control, avoid clashing the dumbbells at the top, and use full range of motion to target the pecs through every rep.
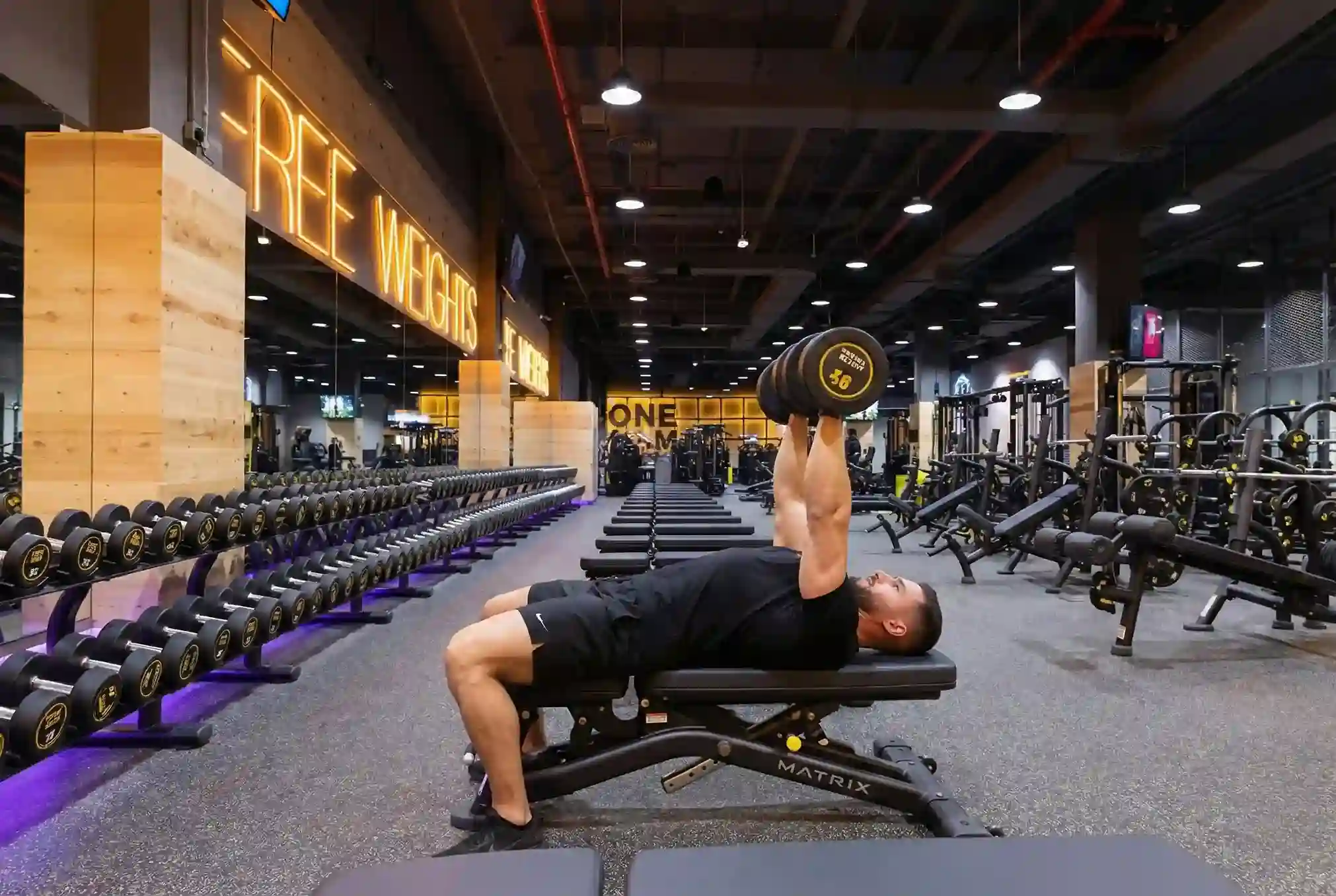

Personal Trainer Notes:
-
Keep wrists straight and stacked over the elbows.
-
Maintain proper form: elbows tucked, palms facing, stable grip, controlled lowering.
-
Keep knees, feet, and upper back stable to support alignment.
-
Focus on smooth motion and constant tension — don’t drop the weights.
-
Use a spotter when pressing heavier loads or approaching fatigue.
-
Good form helps avoid shoulder issues and ensures the correct muscles are targeted.
Additional Strength Benefits & Variations
Why lifters choose dumbbells over barbells:
- Greater range of motion and muscle stretch
- Improved chest muscle activity
- Less stress on the shoulder joint
- Increased core stability
- Helps build unilateral strength and correct asymmetries
- Reinforces proper technique and joint positioning
Useful variations
- Incline dumbbell bench press for clavicular head emphasis
- Flat bench press for mid-chest strength
- Floor dumbbell press when no bench is available
- Single-arm dumbbell pressing for targeted stability training
Each variation supports different fitness goals, enhances muscular balance, and builds foundational pressing strength that carries over to barbell movements.

TRY GYMNATION FOR FREE
GET YOUR FREE DAY PASS at the BEST GYM IN THE GCC
Thank You,
YOU WILL RECEIVE A CALL FROM EITHER OUR UK (+44) CALL CENTRE OR A UAE (+971) OR KSA (+966) MOBILE NUMBER
Alternative Chest Exercises
Dumbbell Bench Press FAQs
Yes — it improves range of motion, increases chest activation, strengthens the triceps, promotes better shoulder stability, and helps fix imbalances created by traditional barbell bench movements.
Main targets:
-
Pectoralis major (clavicular and sternal heads)
-
Triceps brachii
-
Anterior deltoid
Stabilisers:
-
Serratus anterior
-
Rotator cuff muscles
-
Scapular stabilisers (middle and lower trapezius, rhomboids)
-
Core musculature
Choose a load you can control through the full rep range without flaring elbows or breaking proper form. If control is lost, reduce weight.
Neither is universally better. Dumbbells allow more range of motion, enhance unilateral strength, reinforce technique, and can reduce shoulder stress. Barbells allow heavier loading — both should exist in a balanced strength-training plan.
-
Muscle mass: 3–4 sets × 8–12
-
Strength: 4–5 sets × 4–6
Use controlled reps, strong tension, and progressive overload.
Yes — the dumbbell floor press still trains the chest, triceps, and shoulders, though range of motion is reduced.