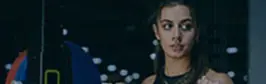Dumbbell Single Leg Split Squat
Dumbbell Single Leg Split Squat Video Guide
The Dumbbell Single Leg Split Squat is a powerful unilateral exercise that targets the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and core. By placing the load primarily on one leg, it improves lower body strength, corrects muscle imbalances, and enhances stability. This variation of the dumbbell split squat works the front leg through a deeper range of motion, while the rear foot supports balance without taking over the movement.
How to Perform the Dumbbell Single Leg Split Squat
-
Start in a split position with your front foot a few feet ahead and dumbbells at your sides.
-
Lower your back knee toward the floor by bending the front leg while keeping your torso upright.
-
Maintain a slight forward lean from the hips without rounding.
-
Push through the front heel to return to standing.
-
Complete your reps on one side before switching legs.
GymNation Tip: Think elevator, not escalator—drop straight down, stay balanced, and drive through the front heel to keep the tension on your glutes, not your lower back.

Personal Trainer Notes:
-
Keep your front knee aligned over the foot—avoid collapsing inward.
-
Your back foot should stay light; drive with the working leg.
-
Slow, controlled reps increase muscle growth and stability.
-
Use heavier weight only when balance and form are solid.
-
Ideal on leg day for building strength without heavy spinal loading.
TRY GYMNATION FOR FREE
GET YOUR FREE DAY PASS at the BEST GYM IN THE GCC
Thank You,
YOU WILL RECEIVE A CALL FROM EITHER OUR UK (+44) CALL CENTRE OR A UAE (+971) OR KSA (+966) MOBILE NUMBER
Alternative Glute Exercises
Dumbbell Single Leg Split Squat FAQs
The dumbbell single leg split squat targets the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and core stabilisers. Because it’s a single leg squat pattern, it improves balance and fixes muscle imbalances more effectively than a traditional squat.
Start with the front foot planted, the rear leg positioned behind you, and hold dumbbells by your sides. Lower the back knee toward the floor while keeping the torso upright. Push through the front heel to stand. Maintain a stable starting position and full range of motion.
Benefits include increased leg strength, improved lower body stability, better glute activation, reduced reliance on spinal loading compared to barbell squats, and correction of strength differences between the weaker side and dominant side.
Common dumbbell single leg split squat variations include the Bulgarian split squat (rear foot elevated) using a bench or plyometric box, front foot elevated split squat, tempo split squats, and goblet split squats using a single dumbbell.
No. A split squat keeps both feet fixed in place, while a lunge involves stepping forward or backward. The split squat allows more focus on the front leg and improves control in the bottom position.
No. A dumbbell single leg squat (pistol squat) requires full bodyweight support on one leg, while the split squat uses the rear foot for balance, making it a more accessible but still highly effective lower body exercise.